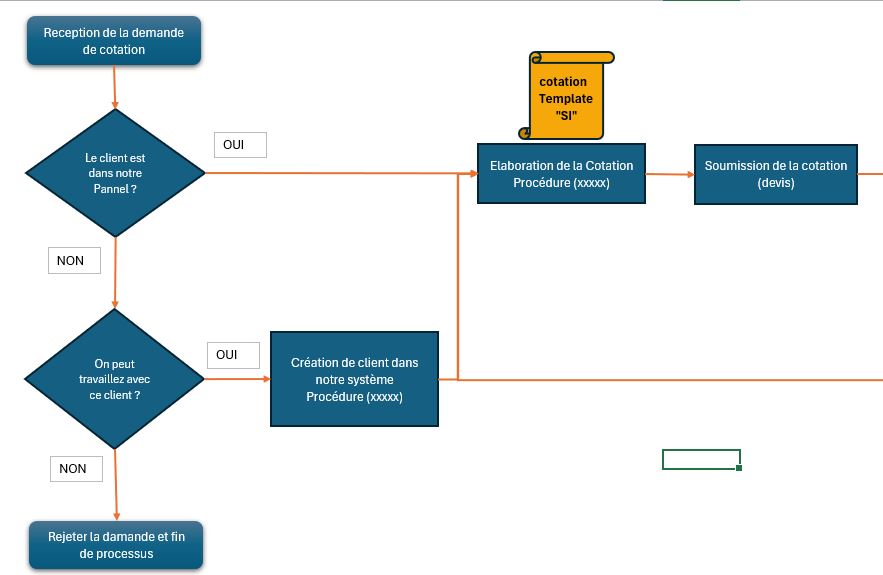
Business Process Modeling: A Blueprint for Efficiency In today's dynamic business environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge. Business Process Modeling (BPM) offers a powerful approach to visualize, analyze, and improve business processes. By creating visual representations of workflows, BPM enables stakeholders to understand how processes function, identify bottlenecks, and implement changes for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness. What is Business Process Modeling? Business Process Modeling is the graphical representation of a company's business processes and workflows. It involves creating a visual map of activities, decisions, and information flows within an organization. These models serve as a blueprint for understanding, analyzing, and improving processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and better outcomes. Why is Business Process Modeling Important?
- Improved Understanding: BPM provides a clear and concise view of complex processes, making it easier for everyone to understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Bottleneck Identification: By visualizing the process flow, it becomes easier to identify areas where delays, redundancies, or inefficiencies occur.
- Process Optimization: BPM allows for the simulation of different scenarios and the evaluation of potential improvements before implementation.
- Better Communication: Visual models facilitate communication and collaboration between different departments and stakeholders.
- Compliance and Auditability: BPM helps organizations document their processes, making it easier to comply with regulations and prepare for audits.
Common BPM Notations and Tools Several notations and tools are available for business process modeling. Some of the most popular include:
- Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN): A standardized graphical notation for representing business processes. BPMN is widely used due to its versatility and expressiveness (OMG, 2024).
- Unified Modeling Language (UML): A general-purpose modeling language that can be used for BPM, particularly for processes involving software development.
- Flowcharts: Simple diagrams that use symbols to represent steps in a process.
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): A lean management technique used to analyze and improve the flow of materials and information required to bring a product or service to a customer.
Popular BPM tools include:
- Microsoft Visio: A widely used diagramming tool that supports BPMN and other modeling notations.
- Bizagi Modeler: A free tool specifically designed for BPMN modeling.
- Bonita BPM: An open-source BPM platform that includes modeling, execution, and monitoring capabilities.
- Camunda: An open-source platform for workflow and decision automation.
Steps in Business Process Modeling
- Identify the Process: Define the scope of the process you want to model.
- Gather Information: Collect data on the process, including activities, inputs, outputs, roles, and rules.
- Create the Model: Use a BPMN tool or other notation to create a visual representation of the process.
- Analyze the Model: Identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Implement Changes: Modify the process based on your analysis and implement the changes.
- Monitor and Refine: Continuously monitor the process and make further refinements as needed.
Conclusion Business Process Modeling is an essential practice for organizations seeking to improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive advantage. By visualizing and analyzing their processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement changes that lead to better outcomes. With the right tools and techniques, BPM can transform the way businesses operate, driving innovation and growth. Reference
- OMG. (2024). Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). Retrieved from https://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/2.0/


